Recent security monitoring has shown an increase in unauthorised attempts to access client’s hosting accounts. In light of this, this article will examine why you need to keep your account secure and explain the measures we recommend to protect it from hackers.
Contents
Why it’s important to keep hosting accounts secure
Logging into your hosting account (client area) enables you to access a wide range of information and carry out numerous actions. This is where your personal details are held, including financial information for paying your hosting bills, contact details and records of transactions. If a hacker had access to your client area, this information could be used in a number of malicious ways. These can include using your banking details to make illegal purchases or using your personal information to make phishing attacks against you seem genuine, increasing the risk of you being defrauded.
If that isn’t worrying enough, access to your hosting account gives hackers the ability to change passwords and block you from your account. Once this is done, they will have full access to your website controls, data and files, enabling them to make changes to your website, install malware, redirect or create new domains, redirect payment gateways, set up email addresses, and carry out a whole host of other activities. If you’re not someone who checks their website or hosting account very often, they can even take out new services with your host, such as purchasing a server on which to run illicit operations and do so using your banking details.
Overall, the consequences of someone hacking your hosting account can be extremely serious, including data breaches, financial loss and major damage to your company’s reputation.
Is your email secure? Read How to Protect Against Email-Related Data Breaches
How hackers gain access
Modern hackers can use a range of different methods to attempt to gain access to your hosting account. Three of the most common are phishing attacks, credential stuffing and brute force attacks.
Phishing attacks, which usually arrive as emails, are exceptionally common. Typically, they will pretend to come from your hosting provider and tell you that there is a problem that needs urgent attention, such as you need to verify your account to stop it being closed or that there is an unpaid bill that needs settling. After creating a sense of urgency, the email then contains a link to your account to help you respond quickly. The link, however, is to a fake website that looks like your web host’s login page. Once you enter your login credentials, they will be sent directly to the hacker. In the meantime, the fake page will take you to the real login page as soon as you hit enter. You are led to believe there’s been a glitch with the login but are none the wiser about being the victim of the phishing scam. With your credentials, the hacker now has access to your hosting account.
You should also be aware that phishing scams can be carried out by text message and telephone. With the latter, the scammer will pretend to be from your hosting provider and will ask to take you through security before proceeding with the call. The security questions you are asked are designed to get your login credentials from you.
For more information, read: How to Protect Your Business from Phishing
Credential stuffing is a technique where hackers use previously leaked or stolen usernames and passwords to access accounts. Success here relies on two things – firstly that you use the same login credentials for your hosting account for other online accounts, and secondly that one of those other accounts has suffered a data breach that included your user details. Data breaches are more common than you think and there are millions of leaked login credentials available on the dark web, many of them for free, giving cybercriminals easy access to them. If you never use the same password twice for different accounts, this kind of attack is useless against you. Thankfully, many password managers, including Google’s, will now tell you if any of your login details have been discovered in a breach or found on the dark web, enabling you to make appropriate changes.
In a brute force attack, hackers use specialist software that makes repeated guesses at your password and username. This might seem like an impossible feat, however, using databases of stolen credentials and sophisticated algorithms, these tools make highly educated guesses rather than random ones. Weak or common passwords can be cracked in minutes. As these tools make lots of guesses in a very short space of time, they are often detected and blocked by your web host’s firewall. However, they will try to prevent detection by using VPNs that change their IP address, so it looks like each attempt is from a user in a different location.
Of course, there are other ways that hackers can get hold of your login details. Sharing them with others increases their vulnerability as does storing them insecurely on devices. If you save them as a file on your computer or phone and one of those gets hacked, then they are easy to discover.
For more information, read: 5 Ways to Improve Your Website Security
Keeping hackers at bay
The first step towards making your hosting account secure is to create a strong and unique password. By unique, we mean that you do not use it for any other online account. By strong, we mean creating a password that would be incredibly difficult for either a human or a sophisticated software tool to guess. This essentially means using a random mix of lower and uppercase letters, numbers and allowable special characters. For important accounts like your client area, aim for at least 16 characters in the password – the longer it is, the harder it is to crack. Today, most computers and phones will offer to suggest strong passwords for you and will store them securely in a password manager, saving you the need to memorise them or store them somewhere unsafe.
Strong passwords on their own cannot guarantee that your account remains secure. To make it virtually impossible to hack into your hosting account, you need to implement an additional layer of security. The best way to do this is by implementing two-factor authentication (2FA).
2FA requires you not only to input your username and password; it also requires further proof that you are authorised to access the account. The most common form of proof is to input a six-figure code. Depending on the 2FA solution you use, this can be emailed or texted to you, or it can be generated by an app, like Authenticator, on your phone. While the code is important, what is actually verified is that you are in physical possession of the phone or have access to the email address linked to the account.
For additional assurance, these codes have a very limited time span, usually only around 30 seconds. This prevents hackers from using older codes stored on your devices to gain access and means brute force tools don’t have enough time to crack the code before it changes. Besides codes, other forms of verification in use include physical tokens and biometric details like fingerprints and facial recognition.
While we understand that some clients find using 2FA a chore when logging in, given the risks, it is worth the extra effort. Indeed, implementing 2FA significantly reduces the chance of someone gaining unauthorised access to your hosting account.
Implementing 2FA
If you haven’t yet set up 2FA on your eukhost hosting account, you can do so by following the instructions below:
- Before you start, you will need to install an authentication app on your mobile phone, tablet or PC. We recommend either Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator. These apps are free and can be downloaded from either the Google Play Store or Apple’s App Store.
- Once your chosen app is downloaded and installed, log into your eukhost client portal.
- In the dropdown menu, under your name at the top of the page, select 2FA/Security Settings.
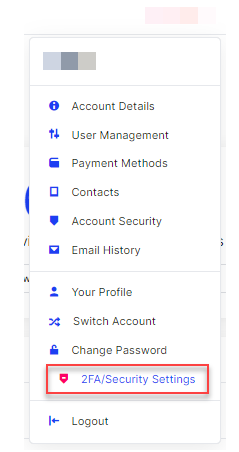
- Click on the Click Here to Enable button.
- When the screen opens, click Get Started and a QR code will appear on the screen.
- Using the authenticator app, scan the QR code or enter the provided code manually into your app.
- The authenticator app will then generate a six-figure code. Enter this code in the box provided on your client portal and click Submit. 2FA will now have been set up for your account. When you next log in, you will need to use the code displayed on your authenticator app. These are time-limited and change around every 30 seconds.
When setting up 2FA, you will be provided with a set of backup codes. These are for emergency use should you lose the device on which the authenticator app is stored. They should be saved and stored securely.
Conclusion
Given the range of threats hosting accounts face today, and the risks associated with unauthorised access, improving login security is absolutely vital. While strong passwords are an important step in the right direction, implementing two-factor authentication is a more robust and effective way to keep your client area secure.
Suspicious Activity? Contact Us Immediately
Should you ever receive a suspicious email or call regarding your account, or notice any suspicious activity, don’t hesitate to contact us immediately through phone or live chat on our official website.



